The basic concept of Insurance is offsetting the risk. Insurance is a readable contract. There are some types of insurance contracts in which if you return to the Insurance company, you will receive money against it. But basically, Insurance is A contract that helps them offset the risk.
There are many different types of risks related to our life. Some of them are very Small some of THEM are Big. It is like a possibility of the occurrence of specific events. The answer to why I need Insurance was written on the Wells Fargo website.
“Even if you’re in Good health, an unexpected illness or injury could require you to out of pocket if you don’t have health insurance. If you are uninsured and unexpectedly require surgery or other emergency care your expense will be for the full amount of the service which could be thousands of dollars.” – Wells Fargo
The picture is the same everywhere, which is the insurance industry’s starting point.
In India, 49% of FDI is allowed from 2014. But still the largest Life insurance company in India, LIC is held by Govt As per the Constitution of India, Insurance comes under the Seventh Schedule of Union List. This means only Centra Government can regulate the insurance Sector.
History of Insurance Industry in India
The history of Insurance in India can be Tracked back to the Vedas. In manusmriti, we find various forms of Insurance mentioned. For example, Yogakhema, Headquarters of Life Insurance Corporation of India, is derived from Rigveda.
Bombay Mutual Assurance Society was, First insurance society formed in 1870.
Insurance in its current form has its history dating back to 1818. Anita Bhavsar, Started Oriental Insurance Company to cater European Community. In 1956, the Government of India consolidated 245 insurance entities, including Foreign Insurance and provident institution, and made a Life insurance corporation. In 1972, the General Insurance Business nationalization act passed And came into effect on 1 Jan 1973. Till the 90s, LIC and GIC were Monopoly. GIC was operating through four subsidiaries. In December 2004, All five of THEM were different insurance companies, namely Oriental Insurance Company, New India assurance company limited, National Insurance Company Limited, and United India Insurance Company Limited.
Industry Structure
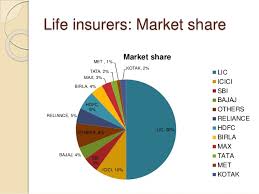
Against the global average of 75% in India, less than 2% of people are insured with some scheme. As the second-largest country in the world, the projected market for Insurance in India is US$ 350 – 400 Billion by 2020. The industry consists of 53 companies, where 24 are in life insurance, and 29 are in non-life Insurance. LIC is the only Govr own life insurance company, and there is a Single Reinsurance company GIC re. Among the most prominent private Insurance companies, ICICI Prudential and HDFC Standard Life insurance are essential. In addition, there are two specialized Public Sector Insurance Companies, namely Export Credit Guarantee Corporation for credit insurance and agriculture insurance company for Crop insurance.
April 2015– March 2916 insurance industry grow by 22.5 %, with ₹1.38 trillion as new Premium. General Insurance increases by 12%. Gross Direct Premium underwrite in 2016 April as ₹106 Billion.
The insurance market is expected to quadruple in the next ten years. Therefore, the Indian Insurance market is a massive opportunity as the penetration and the percentage of an insured population are low.
Operations
Insurance Companies are intermediaries as they connect the customer, investor, Creditors, and reinsurers willing to bear the risk. So insurance companies are pivotal in transferring risk to sturdy shoulders. They Also maintain Investments to take care of the risk. The company also held a diversified portfolio of related insurance contracts. Diversification reduces the risk for the company. The loss rate in a well-diversified portfolio is predictable and manageable often for the company itself. Auto insurance is relatively riskier as the risk here doesn’t correlate. Even in that case, Diversification helps. So when anyone is buying the stock of Insurance companies, he is taking part of that very much low risk, which is well-diversified with reinsurance, Investment against it, and sufficient Premium collected from Insurer which also includes running and financing the cost of the company.
As insurance companies are long-term investors, they invest in many different assets. But often, the market is giving around half of the market value as they will not sell investment tomorrow.
Valuing the insurance company is much like valuing perpetuity. They will continue to receive the Premium for a long time, so if you know how to find the present value of all that Future Cash flow. You are just done.