Insurance companies are complicated to understand and analyze. It is an A task. The reasons vary due to terminology, calculation, different ways to show results, and the nature of business. One ratio is an example of this. It is the Loss ratio.
Maybe you are all confused right now like I was when I first heard about it. It is not at all problematic. Is one, on the contrary, the most important ratio for analyzing Insurance companies? But still, I can’t find it used in India when it comes to investigating insurance companies. We Indians are not studying them. We are making gungho for HDFC where Parent is good even though capital adequacy is terrible, not good market share, etc.
So What is the Loss ratio?
In insurance industry, The insurance companies collect premium for entering into contract for sharing risk of something. say Risk of loosing Car. In that contingency, the company will pay Amount decided. For all of this they incur costs like administrative cost, plus Commission. But They are small. Real large part is Amount paid ( Claims ) to policy holders.
This is the thing why insurance companies are challenging to analyze. Two different accounts. What to analyze. What am I doing? Examining the policyholder’s account.
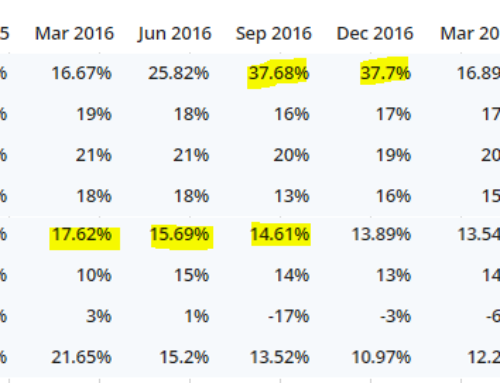
So Calculating how the large amount is paid out of the Collected premium is making a significant ratio, and that is all about what we are doing here.
Why is this important?
The loss ratio is a measure used in insurance to indicate the percentage of claims that an insurer pays out relative to the premiums it receives. It is calculated by dividing the total amount of claims paid by the insurer by the total premiums collected over a specific period of time, typically a year. The resulting percentage represents the loss ratio for that period.
Now some people can claim that insurance companies earn from their investments. I completely agree. But that is not their business. In India, there is something called ULIPs. In my, they are INVESTMENTS and NOT INSURANCE. So if you are analyzing a company like SBI life, it looks like an Asset Management Company AKA Mutual Fund Company. Why am I calling it? Because the moment you start paying Claims from the investment, you can manage your business. You are not profitable. And why are you even there if you are not even beneficial at the gross level?
For example, if an insurer collects $100,000 in premiums over a year and pays out $60,000 in claims during the same period, the loss ratio would be 60%. In this case, the insurer would be paying out a relatively high proportion of the premiums it collects in the form of claims.
Loss ratios are an important measure for insurers, as they can indicate the financial health of the company. If the loss ratio is too high, it may indicate that the insurer is not pricing its policies correctly, or that it is experiencing a higher-than-average number of claims. This can lead to financial problems for the insurer if it is not able to generate sufficient profits to cover its expenses.
On the other hand, if the loss ratio is too low, it may indicate that the insurer is pricing its policies too high, or that it is experiencing a lower-than-average number of claims. This can lead to financial problems for the insurer if it is unable to attract enough policyholders to generate sufficient premiums to cover its expenses.
In general, insurers aim to maintain a loss ratio that is within a certain range that is considered to be financially sustainable. This range will vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of insurance being offered, the specific market in which the insurer operates, and the level of competition in that market.
There are several strategies that insurers can use to manage their loss ratios. One approach is to adjust the premiums charged for its policies to better reflect the risks being covered. This can involve using advanced risk assessment tools to more accurately predict the likelihood of claims being made.
Insurers can also take steps to reduce the number of claims being made. This can involve implementing loss prevention measures, such as providing safety training or safety equipment to policyholders or working with policyholders to identify and mitigate potential risks.
Another approach that insurers can use to manage their loss ratios is to adjust the terms of their policies. This can involve increasing deductibles, co-payments, or other out-of-pocket expenses that policyholders must pay when making a claim. By doing so, insurers can reduce the overall cost of claims, which can help to lower the loss ratio.
Overall, the loss ratio is an important measure that insurers use to assess the financial health of their business. By managing their loss ratios effectively, insurers can ensure that they are able to sustain their operations and remain financially viable over the long term.